|
|
|
•Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A symmetric-key block cipher algorithm for secure classified encryption and decryption.
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS): Software developed by Microsoft designed to provide applications with Single Sign On capability by leveraging Claims-based authentication.
Authentication: Any process by which a system verifies the identity of a User/Entity who wishes to access it.
Authorization: The process by which a system grants permission to a User/Entity for a resource.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): A language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language.
Claims-based authentication: An authentication mechanism that uses Authentication tokens (Claims) to describe a given identity. The process begins with a given identity attempting to access a resource. That resource refers the authenticating entity to a trusted external Claim generating system, A Security Token Service (STS). The Claims are generated by the STS after an identity successfully authenticates. That token is then presented to the desired resource; which will authorize the identity based on the Claims created by the STS.
Email: Messages distributed electronically over communications networks.
Endpoint: A WCF service definition that specified where the protocol, address, port, and path to a service as well as describing how the service is secured.
ETL: Acronym for the industry term Extract, Transform, and Load. A process that involves extracting data from a source, transforming it to fit operational needs, and loading it into the end target (such as a database).
Exception: An exception is a condition that occurs in the operation or the execution of jobs in which either an unexpected or undesirable condition has occurred. Exceptions are stored in the pasTransfer application database when possible and viewable through the user interface or written to the Windows Event viewer when diagnostics mode is enabled or the database is unavailable.
Federated: The means of linking an entity’s identity and its attributes across multiple distinct identity management systems. The application of this concept is used in Claims-based authentication mechanisms.
FTP: File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet.
Hash Function: Any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size.
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): A standardized system for tagging text files to achieve font, color, graphic, and other presentation effects on World Wide Web pages.
JavaScript: An object-orient programming language commonly used to create interactive interfaces within web browsers.
Macro: A small piece of interpreted code used by the system to allow for simple, programmatic access to simple functions and control structures when developing script code.
Mapping: A data table used to identify how source accounts should be transformed into destination data.
pasProtect: The licensing component used in the pasUNITY Enterprise Suite to selectively activate product features using either license files or license codes activated over the Internet.
pasTransfer: An accounting-centric ETL (extract/transfer/load) tool in the pasUNITY Enterprise Suite of applications. It offers advanced features such as mapping, auditing, and lookups in addition to the base ETL functionality. When installed on the same server as pasUnity there are additional service integration menus that will appear in pasUnity to control it and job steps to interact with it.
pasUnity: A set of tools in the pasUNITY Enterprise Suite that allows end users to implement end-to-end process automation solutions with an easy to navigate, easy to use graphical user interface. It has functions for hosting web services, interacting with POP3/SMTP mail systems, launching external processes, centralized reporting, remote management, scheduling, and more.
Public Key Cryptography Standards (PKCS): Specifications produced by RSA laboratories for the use of public-key cryptography. Public-key cryptography uses a pair of keys; one to encrypt and another to decrypt messages so that they arrive securely.
Processing Style: A method of processing source values as either Normal, Credits, Debits, or Reversed.
Really Simple Syndication (RSS): A standardized format used to publish frequently updated information via the web.
Rivest Cipher (RC4): A symmetric key cipher with known security vulnerabilities.
SAML: Security Assertions Markup Language. The standard for creating XML representations of Claims used in Claims-Based authentication.
Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA): Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) compliant family of cryptographic hash functions published by NIST.
Service: A service (or Windows Service) is a software component that is capable of logging into a host operating system and performing working under its own security context and workspace without requiring a user to be interactively logged on to the host.
Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS): A protocol for communication over computer networks utilizing SSL or TLS to encrypt the traffic.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): A standardized security technology for establishing encrypted links between parties. It relies on public-key cryptography. The standard has been deprecated due to security vulnerabilities. Replaced by TLS.
Security Token Service (STS): A software based identity provider responsible for issuing security tokens, a part of a claims-based authentication and authorization system.
Single Sign On (SSO): An entity authentication process that permits a single instance of said authentication to be used for accessing multiple resources or applications.
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE): A technology employed by Database Management Systems to encrypt databases at the file level.
Transport Layer Security (TLS): A standardized security technology for establishing encrypted links between parties. It relies on public-key cryptography. Designed as a replacement for the deprecated SSL standard.
UI: User Interface. Any application component which interacts with a user.
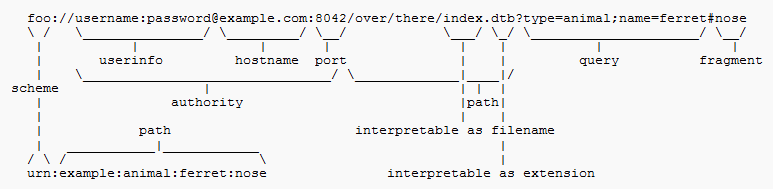
URL: A URL is an acronym for Uniform Resource Locater and is a string of characters that provides minimally a schema and a host name. The full syntax of a URL appears below. A simple example would be http://www.pasportal.com
WCF: WCF is an acronym for Windows Communication Foundation and is a set of technologies used for hosting XML-based services on Windows-based operating systems.
Wildcard: A character or string of characters that can be used to substitute for any of a defined subset of all possible characters when using pattern-matching functionality.
XML: Extensible Markup Language is a markup language (similar to HTML) that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that both human and machine readable. XML is commonly used to define documents with a standard format that can be read by any XML-compatible application such as web services.
Copyright © 2025 pasUNITY, Inc.
Send comments on this topic.